What I am always thinking about COVID-19 was written in the following paper published from a group of Central University of Tamil Nadu etc.
https://academic.oup.com/femspd/article/79/1/ftaa076/6027506
In the case of COVID-19, there are so many asymptomatic individuals (some studies have estimated that up to 80%).
Generally speaking, the incubation period for COVID-19 is reported to be between 5 to 6 days, although this can be up to around 14 days, but, asymptomatic individuals show an extended median duration time of 19 days.
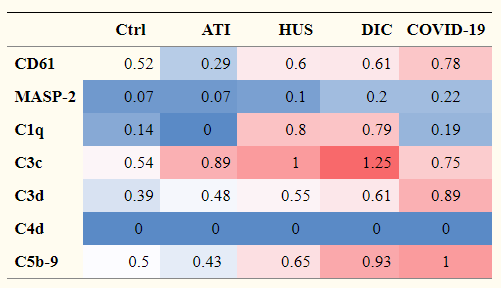
SARS-CoV-2 activates the STING pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome assembling, and induces cytokine storm as a result of excess production of IL-1β, and IL-18, TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-6, etc. However, bats do not develop any disease, although they are reservoir of various viruses. In the case of bats, they are coexisting with virus preparing the following features evolutionally.
(1)limiting the assembly of the NLR family pyrin domain containing three (NLRP3) in monocytes、
(2)loss of the ability to effectively sense exogenic cytoplasmic DNA via loss of PYHIN genes
(3)excessively high levels of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10,
(4)lack of functional killer cell Ig-like (KIR) and killer cell lectin-like (KLR) receptors.
It is know that the levels of inflammatory cytokines are relatively low, and the SARS-CoV-2-specific IgG and neutralizing antibody levels are significantly lower in asymptomatic individuals. This might mean that asymptomatic is a result of weak immune response. And on the contrary, it might be a result of existing antibody cross-reactivity of classical seasonal cold-causing coronaviruses 229E, HKU1, OC43 and NL63.
In the context of coexistence with virus, mechanisms uncovered in bats likely hint the development of therapeutic strategies against COVID-19 in humans. That could be a wisdom, to survive virus wars.